A digital stamp for contactless certification
The combination of a high-precision marking technique, developed by a UNIGE spin-off, and a tamper-proof digital certification system enables any valuable object to be authenticated and tracked.
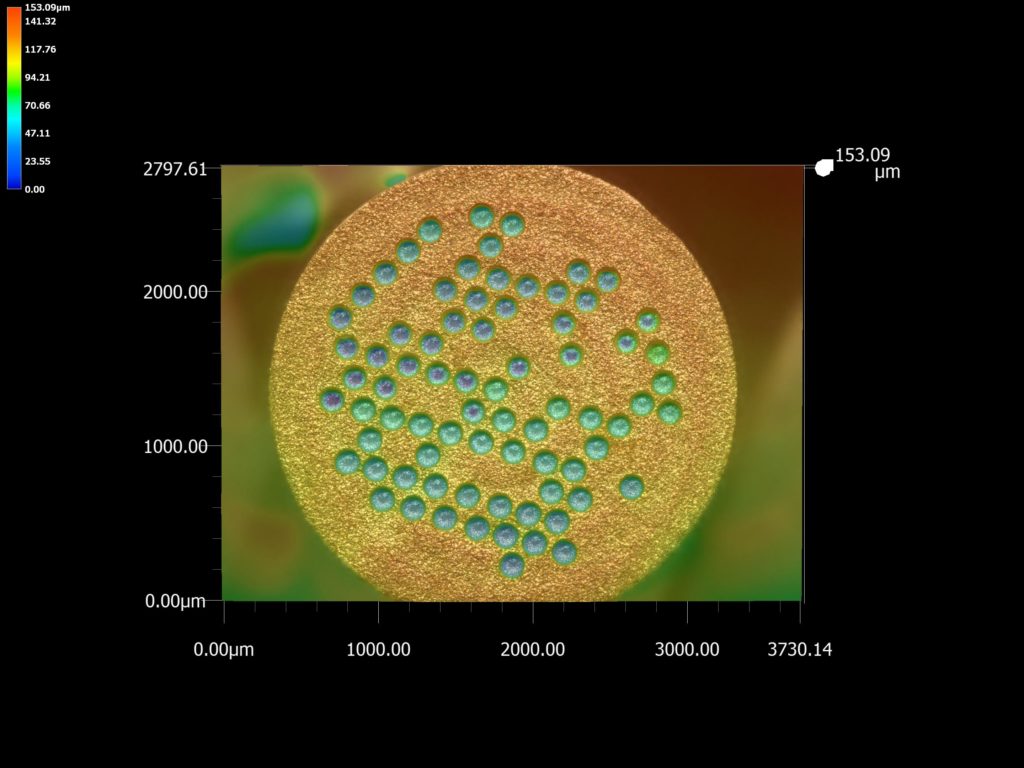

An aesthetically pleasing miniature engraving, without burrs, that can be applied to any metal and represents a code that gives access to a tamper-proof digital safe, which contains all the information you wish to place inside: this is the ultimate hallmark, the marking that provides the flawless traceability and authentication that manufacturers of high-value-added objects dream of, from the watch and jewelry industry to the aerospace and medical instruments sectors. This cutting-edge anti-counterfeiting technology will be previewed on 12 October 2023 at the “Autour du temps” watchmaking know-how days in Plan-les-Ouates. It combines, on the one hand, a digital certification system in the form of an NFT (non-fungible token) using a blockchain (a computer technique on which cryptocurrencies are based) and, on the other, an ultra-precise, contactless engraving method. The first was developed by a small French company, Ocode. The second was developed by physicists at the University of Geneva as part of the National Centre of Competence in Research on Materials with New Electronic Properties (MaNEP), and is marketed by Phasis, a UNIGE spin-off co-founded and directed by Jorge Cors, project leader in the Department of Quantum Matter Physics (DQMP, Faculty of Science). Together, the two technologies form a discreet digital hallmark that is easy to affix and represents a code linked to a confidential certificate of authenticity that is unique to each marked object.
Read more in the UNIGE’s Journal